|
|
| New progress in potentiometric biosensing for bacteria |
Polymeric membrane ion sensors have new breakthroughs in sensitivity, selectivity and stability. However, it is still a big challenge to achieve the direct potentiometric sensing of analytes using the hydrophilic bioreceptors. The research group led by QIN Wei at the Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research has developed a magneto-controlled potentiometric sensing system based on hydrophilic bioreceptor-assembled magnetic beads. The potentiometric assay relies on the intrinsic charges of an antimicrobial peptide and its unique recognition abilities, which can eliminate the probe labelling and indicator addition. Staphylococcus aureus, as a model of food-borne pathogens, was measured at levels down to 10 CFU mL-1. To expand the applications of this methodology, one disposable potentiometric sensor array for use as an “electronic tongue” was designed to achieve multiple bacteria classification and identification in a rapid way. The present methodology is simple, general and versatile and can pave a new way to develop label-free potentiometric sensing assay for sensitive and selective detection and identification of various targets. 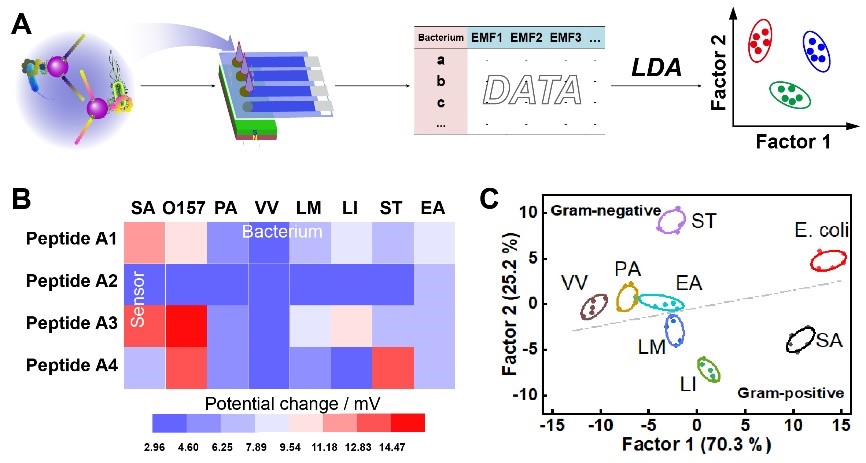
Schematic illustration of the potentiometric sensor array for multiple bacteria classification and identification Citation: Enguang Lv,+ Yanhong Li,+ Jiawang Ding,* and Wei Qin*, Magnetic Field-Driven Extraction of Bioreceptors into Polymeric Membranes for Label-Free Potentiometric Biosensing, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2609-2613. Link:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202011331 |
|